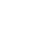Chemical composition and properties of 316 stainless steel mesh
Model, chemical composition and performance of 316 stainless steel wire mesh
Due to the addition of Mo element, 316 stainless steel has greatly improved its corrosion resistance and high temperature strength. The high temperature resistance can reach 1200-1300 degrees, and it can be used under harsh conditions.
316 stainless steel wire mesh performance: the corrosion resistance is better than 304 stainless steel, and it has good corrosion resistance in the production process of pulp and paper. Moreover, 316 stainless steel is also resistant to erosion by marine and aggressive industrial atmospheres.
Heat resistance: 316 stainless steel (06Cr17Ni12Mo2) has good oxidation resistance in intermittent use below 871 °C (1600 °F) and continuous use above 927 °C (1700 °F). In the range of 427°C-857°C (800°F-1575°F), it is best not to use 316 stainless steel continuously, but when using 316 stainless steel continuously outside this temperature range, the stainless steel has good heat resistance. The carbide precipitation resistance of 316L stainless steel is better than that of 316 stainless steel, and the above temperature range can be used.
Heat Treatment: Anneal in the temperature range 1850-2050°F, then rapidly anneal, then rapidly cool. 316 stainless steel cannot be hardened by heat treatment.
Welding: 316 stainless steel has good welding performance. All standard welding methods can be used for welding. According to the application, 316Cb, 316L or 309Cb stainless steel filler rods or welding rods can be used for welding. In order to obtain the best corrosion resistance, the welded section of 316 stainless steel needs to be annealed after welding. If 316L stainless steel is used, post-weld annealing is not required.